
 SB431542
SB431542
S1067
5~200mg
Brand
Selleckchem
Description
SB431542
SB431542 is a potent and selective inhibitor of ALK5 with IC50 of 94 nM, 100-fold more selective for ALK5 than p38 MAPK and other kinases.

Biological Activity
| Description | SB431542 is a potent and selective inhibitor of ALK5 with IC50 of 94 nM, 100-fold more selective for ALK5 than p38 MAPK and other kinases. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targets | ALK5 | |||||
| IC50 | 94 nM [1] | |||||
| In vitro | SB 431542 inhibits the activin type I receptor ALK4 and the nodal type I receptor ALK7, which are responsible for the phosphorylation of Smad2. SB 431542 has little effect on ALK1, ALK2, ALK3, and ALK6, which show phosphorylation of Smad1. SB 431542 is a selective inhibitor of endogenous activin but has no apparent effect on BMP signaling. SB 431542 could induce both Smad2/Smad4- and Smad3/Smad4-dependent transcription.[2] In A498 cells, SB 431542 inhibits both TGF-β1-induced collagen Iα1 and PAI-1 mRNA with IC50 of 60 nM and 50 nM, respectively. In addition, SB 431542 inhibits production of TGF-β1-induced fibronectin mRNA and protein with IC50 of 62 nM and 22 nM, respectively. [3] SB 431542 blocks the TGF-β-mediated growth factors, including PDGF-A, FGF-2 and HB-EGF, leading to an increase in proliferation of MG63 cells. SB 431542 also inhibits TGF-β-induced c-Myc and p21 WAF1/CIP1. [4] SB 431542 significantly suppresses TGF-β-induced G1 arrest, leading to accumulation of cells in the S phase of the cell cycle in FET, RIE, and Mv1Lu cells. SB 431542 also inhibits TGF-β-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in NMuMG and PANC-1 cells. [5] SB 431542 significantly elevates the expression of CD86 in BM-DCs and that of CD83 within CD11c+ cells suppressed by TGF-β. SB 431542 is able to induce NK activity through functional maturation and IL-12 production of human DCs. [6] | |||||
| In vivo | SB 431542 triggers cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) activities in the colon-26 carcinoma models and is most likely to produce antitumor immunological outcomes through alteration of DC function suppressed by TGF-β. [6] | |||||
| Features | ||||||
Protocol(Only for Reference)
Kinase Assay: [1]
| Flashplate assay for ALK5 | SB 431542 is dissolved in DMSO at a concentration of 10 mM. The kinase domain of TGFβRI, from amino acid 200 to the C-terminus, and the full-length Smad3 protein are expressed as N-terminal glutathion S-transferase (GST) fusion proteins in the baculovirus expression system. Proteins are purified with glutathion Sepharose beads 4B. Basic FlashPlates are coated with 0.1 M sterile filtered sodium bicarbonate, pH 7.6, containing 700 ng of GST-Smad3 per 100 μL. Assay buffer contains 50 mM HEPES (pH 7.4), 5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM CaCl2, 1 mM DTT, 100 mM GTP, 3 μM ATP plus 0.5 μCi/well ɤ33P-ATP, and 85 ng of GST-ALK5 with or without SB 431542. Plates are incubated at 30 °C for 3 hours. The assay buffer is removed by aspiration, and the plate is counted on a Packard TopCount 96-well scintillation plate reader. |
|---|
Cell Assay: [4]
| Cell lines | MG63 and NIH3T3 |
|---|---|
| Concentrations | 0.3 μM |
| Incubation Time | 30 minutes |
| Method | To explore the effects of ligands, MG63 and NIH3T3 cells are seeded at a density of 8 × 104 cells/well in 6-well plates and starved (0.1% FCS for MG63 cells and 0.5% FCS for NIH3T3 cells) for 24 hours before ligand stimulation. Media containing various ligands are exchanged at 48-hours intervals. Cells are trypsinized and counted by a Coulter counter on days 2, 4, and 6 after ligand stimulation. To explore the effects of constitutively active receptors, cells are seeded at a density of 2 × 105 cells/well in 6-well plates. The next day, cells are infected with adenoviruses carrying various cDNAs at a multiplicity of infection of 100. Cells are trypsinized and counted on day 3. Cell proliferation assay is performed in the presence of 0.3 μM SB 431542. |
Animal Study: [6]
| Animal Models | BALB/c mice receive intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections of colon-26 tumor cells. |
|---|---|
| Dosages | 1 μM solution, 100 μL/mouse |
| Administration | Directly injected into peritoneal cavity |
| Solubility | 1% DMSO/30% polyethylene glycol/1% Tween 80, 30 mg/mL |
References
Chemical Information
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 384.39 |
|---|---|
| Formula |
C22H16N4O3 |
| CAS No. | 301836-41-9 |
| Storage | 3 years -20℃Powder |
|---|---|
| 6 months-80℃in DMSO | |
| Syonnyms | N/A |
| Solubility (25°C) * | In vitro | DMSO | 77 mg/mL (200 mM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | <1 mg/mL (<1 mM) | ||
| Ethanol | 3 mg/mL (7 mM) | ||
| In vivo | 1% DMSO/30% polyethylene glycol/1% Tween 80, | 30 mg/mL | |
| * <1 mg/ml means slightly soluble or insoluble. * Please note that Selleck tests the solubility of all compounds in-house, and the actual solubility may differ slightly from published values. This is normal and is due to slight batch-to-batch variations. |
|||
| Chemical Name | 4-(4-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-5-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-imidazol-2-yl)benzamide |
|---|
Preparing Stock Solutions
| Stock Solution (1ml DMSO) | 1mM | 10mM | 20mM | 30mM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass(mg) | 0.38439 | 3.8439 | 7.6878 | 11.5317 |
Customer Reviews (8)
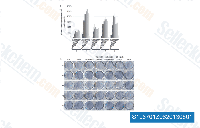 Click to enlarge |
Rating |
|
| Source | STEM CELLS AND DEVELOPMENT, 2013. SB431542 purchased from Selleck | |
| Method | Colony forming assay | |
| Cell Lines | iPS cells | |
| Concentrations | 2 uM | |
| Incubation Time | 18 day | |
| Results | To see if the addition of other small molecule inhibitors improves the efficacy of iPSC induction from myoblast cells in feeder-free conditions, ALK4/5/7 inhibitor SB431542 (SB), MEK inhibitor PD0325901 (PD), nonspecific GSK3 inhibitor lithium chloride (LiCl), and HDAC inhibitor VPA, all reported to enhance the efficiency of iPSC inductions, were tested in combination with NaB (Fig. 2C, D, and Supplementary Fig. S2). Addition of SB to the NaBcontaining medium enhanced the induction efficiency compared with NaB only. Further addition of PD or LiCl to the mixture did not further improve the efficiency. |
Product Citations (3)
-
Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinase (RSK)-2 as a central effector molecule in RON receptor tyrosine kinase mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition induced by macrophage-stimulating protein. [Ma Q, et al. Mol Cancer 2011;10:66]
-
Dioxin receptor expression inhibits basal and TGFβ-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. [Rico-Leo EM, et al. J Biol Chem 2013;288(11):7841-56]
-
Transforming growth factor beta receptor I inhibitor sensitizes drug-resistant pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine. [Kim YJ, et al. Anticancer Res 2012;32(3):799-806]
Application
Reactivity



